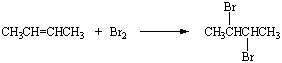Monday, June 6, 2011
Wednesday, June 1, 2011
Functional Groups
-Are specific groups of atoms within molecules that are responsible for the characteristic chemical reactions of those molecules
-Are generally the most reactive part of the molecule
Halogen Compounds
- contain halogen elements such as F, Cl, Br, I.
- are generally insoluble in water
- compounds containing F are inert, Cl and Br are reactive only under the drastic condition, and I are very reactive
Naming the halogen compounds:Follow the standard rules and put a prefixes of a group attached in front of the main-chain name.
F - fluoro Cl- chloro Br- bromo I - iodo
Nitro Compounds
-Lower nitro alkanes are colorless liquids with a pleasant smell. Higher members are solids
-tend to be explosive (ex. TNT)
Naming the rule: Similar to halogen compounds. Put a prefixes of a group attached in front of the main-chain name. ---- NO2 = nitro
 2-Nitropropane
2-NitropropaneAlcohols
-are organic compounds which contain -OH (hydroxyl) functional group.
- are generally colourless liquids at room temperature
- are soluble in water (smaller alcohols are soluble and larger alcohols are insoluble)
-the hydroxyl group makes the alcohol molecule polar
- are poisonous to some degrees
Naming rule: Follow the standard rules and replace the "E" ending in the parent hydrocarbon chain with the ending "OL".

Aldehydes - are the organic compounds that contain double bonded oxygen at the end of the chain-are partially soluble in water-are very reactive Naming rule: follow the standard rules and change the parent chain ending to 'AL'Kentones
-are a hydrocarbon chain with a double bonded Oxygen that is not on either end.
-are typically soluble in water
-carbonyl group is polar
Naming rule: follow the standard rules and change the parent chain ending to 'ONE'
Other Functional groups
•Carboxylic Acids
• Esters
• Ethers
• Amides
• Amines
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)